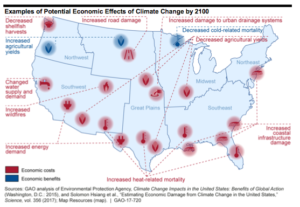
Changing climate will exacerbate global inequalities in health, energy, and labor impacts
New data platform from the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the Climate Impact Lab provides the first empirical, peer-reviewed evidence that climate impacts will fall disproportionately on the poor